Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder walls. It is characterized by rapid (every 15-20 minutes), sharply painful urination in small portions, sometimes with blood impurity, body temperature of subfebrile. The transition of the disease to a chronic form, the climb of infection and the development of the inflammatory process in the kidneys and when decreased in the urethra are possible. When diagnosing cystitis, urine analysis and bladder ultrasound results help the urologist. To determine the etiology of cystysis, bacterial urine sowing is performed and urethral spread. Cystitis therapy implies a predominantly effective effect of the drug on infectious agents that caused it.
Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder mucosa. In most cases, cystitis is infectious. The disease is widespread, affects representatives of the weak and stronger sex, but is more common in women due to some anatomical features of the structure of the female body.
The urethra of women (urethra) wider and shorter than men, so that it is easier for the penetration of pathogens to penetrate the bladder. This determines more frequent cystitis in women. Most often, women for birth are patients with cystitis. There are frequent cases where cystic develops in a woman repeatedly, significantly impairs the quality of her life.
As a rule, cystic is caused by representatives of conditionally pathogenic flora-intestinal stick, streptococci, staphylococci, etc. Cystitis is sometimes found due to infection with pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases-micoplasm and ureaplasm.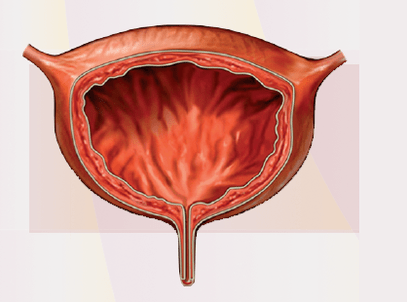
The most characteristic symptom of cystic is painful urination, accompanied by residual sensations of burning and rubbing. In addition, patients with cystitis are impaired by pain in the lower abdomen and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Occasionally, cystitis develops urinary incontinence, which occurs with a strong desire to urinate.
Urine with cystitis can become muddy or gain a reddish shade due to impurities of red blood cells. The temperature sometimes rises to 37, 5 degrees. Increasing temperature with cystitis can signal a possible kidney disease, so in such cases it is urgent to apply for qualified medical care.
Acute cystitis is one of the most common urological diseases. Most often, uncomplicated cystitis is detected, in which germs affect only the mucous membrane without affecting the submucosal layer. According to studies in the field of urology, acute cystitis falls from 26 to 36 million people every year. At the same time, the incidence rate among women is 500-700 episodes per 1000, while among men between the ages of 21 to 50, such an indicator is only 6-8 cases per 1000.
Girls suffer from cystitis three times more than boys. The disease is extremely rare in newborns and children under 1 year of age or more common among children aged 1-3 and 13-15 years. Most often, cystitis is found in children aged 4 to 12 years.
Chronic cystitis also belongs to the number of widespread urological diseases. According to studies, chronic cystitis suffers from 11 to 21% of the population. The significant data dissipation is due to a different approach to determining chronic cystitis. Some studies of studies believe that the diagnosis of chronic cystitis should be made if the frequency of exacerbation is 2 times a year or more, other exacerbations do not specify.
It is unlikely that there is a woman who wants the pleasure of warm summer days to be overshadowed by such an unpleasant disease as cystitis. Meanwhile, in the summer, especially if a woman goes away from home and falls into an unusual environment, there are many causes of cystitis.
The most common causes of cystitis in the warm season:
An additional risk factor for the development of cystitis is sometimes an increase in sexual activity against the background of the following conditions unfavorable to the female body.
If your vacation, however, overshadow the onset of such an unpleasant disease as cystitis, you should urgently contact a urologist. In order to clarify the diagnosis, it will be necessary to undergo ultrasound of the bladder and to analyze the urine. Modern antibacterial drugs effectively affect cystic, can accelerate recovery and prevent the transition of acute cystitis to chronic.
Unlike previous generations drugs that affect the whole body, modern antibiotics used to treat cystitis, selectively act on inflamed tissues of the bladder, practically, without affecting other organs and systems. The concentration of drugs reaches the maximum values only in the urine and the inflamed mucosa of the bladder. This can minimize toxicological loading on the body in the treatment of cystitis and increase the effectiveness of drugs.
Phototoxicity is an unpleasant side effect caused by many medicines to treat cystitis. It manifests itself in increased sensitivity to sunlight, the appearance of redness and burns, even when exposed to ultraviolet rays of low intensity. It develops due to the presence of substances in drugs with the properties of photosensitizers and photoreaches. Such substances lead to the appearance of a large number of free radicals in the skin, which in turn causes the destruction of skin cells, inflammation and burns.
Cystitis can develop at any gestation. The likelihood of cyst development is increased due to the displacement of the internal organs, which are pressed by a growing uterus, changes in the hormonal background and hemodynamics. The impact of these factors causes incomplete emptying of the bladder, and the remains of urine in the bladder serve as a favorable environment for the development of bacteria.
At the first signs of cystitis, a pregnant woman should undergo exceptional consultation of a gynecologist who has a pregnancy and tells him about the symptoms that have occurred. If necessary, the doctor will give the patient a direction to the urologist.
Cystitis can develop in a child of any age, but for girls from old school and school age, the risk of disease is increased by 5-6 times. The main reasons for the frequent development of cystic in children in this group are a number of factors. The ovaries of the girls have not yet begun to produce estrogens, the barrier properties of the mucous membranes are low, and the wide and short urethra allows pathogenic microorganisms to enter the bladder cavity.
The likelihood of cyst development increases in the case of other diseases due to the decrease in immunity and the formation of favorable conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic microbes in the urethra. The main way to prevent cyst in girls is to carefully follow the rules of hygiene.
In 70-95% of patients suffering from acute cystitis, the cause of the disease is converted into a loud stick, in 5-20% of patients Staphylococcus is detected, and in the rest, proe or klebell acts as a pathogen. Typically, cystitis is caused by representatives of conditionally pathogenic flora. With the development of cystitis due to instrumental or surgical interventions, gram -negative bacteria often become the cause of the disease. Studies confirm that cystic pathogens can be not only bacteria, but also viruses, mycoplasmas, trichomons, chlamydia and various fungi.
The widespread cyst in women is due to both the low length and the broad gap of the urethra and its location to other organs. The female urethra, unlike the man, is close to the anus. The anatomical features and topography of the female body contribute to the penetration of pathogens into the urethra, their migration to the bladder and the development of cystitis.
In men, cystitis rarely develops. The cause of cystitis in men usually becomes inflammation of the urethra, prostate gland, appendages of the testes and seminal bubbles. Sometimes urethra infection occurs due to catheterization of the bladder in women and men.
The risk of cystitis increases during catheterization of the bladder in men suffering from prostate adenoma, one of the symptoms of which is a constant slowdown in urine. The risk of cystitis is also increased with the introduction of a pregnant woman's catheter or recently gave birth to a woman, due to a decrease in the tone of the urinary tract.
The rapid healing of cystic and complete restoration of the bladder mucosa is possible with the timely onset of treatment and the use of drugs sufficient efficiency. It should be emphasized that the chances of getting rid of the cystic with timely diagnosis and the use of medicines that detectly detect the pathogens of the infection. Later on to the onset of treatment and prescription drugs that only eliminate the symptoms of cystitis without affecting the pathogenic environment can lead to the transition of acute cystitis to chronic.
The main task facing the doctor who treats cystitis is the destruction of pathogenic microorganisms penetrating the bladder and causes inflammation of the mucosa. The choice of antibacterial cystitis therapy is determined by parameters such as the duration of the disease and the severity of the symptoms. In addition, when choosing medicines, possible side effects, absorption of the drug, the method and the rate of its excretion are taken into account the presence of concomitant diseases, etc.
The effectiveness of the drug in the treatment of cystitis is determined by the ability of this medicine to affect certain microorganisms. It should be remembered that pathogenic bacteria adapt and become insensitive to antibiotics. Over time, the main cause of cystica (E. coli) has become resistant to these drugs. In addition, medicines for the treatment of cystitis associated with the previous generation of antibiotics have a very high level of toxicity and cause various side effects.
When choosing a medicine for the treatment of cystitis, the cost of treatment, which is determined not only by the cost of one tablet, but also by the actual effectiveness of the antibiotic, the duration of intake and the possible risk to the health of the patient, should also be taken into account. Today, there are accessible medicines for the treatment of cystitis, selectively affecting the pathogens of the disease. Once in the body, the medicine is concentrated in the bladder, allowing you to increase its effectiveness. In addition, the use of the latest generation antibiotics provides a reduction in cystitis treatment, reduces the likelihood of side effects and reduces the risk to the patient's body.
In the treatment of cystitis, fat and spicy foods should be excluded from the diet, increase fluid intake and avoid hypothermia. The warm heating pad placed on the lower abdomen helps with cystitis. Complex treatment of cystitis is possible with the use of ionoporesis, UHF or inductionothermia is possible. We should not forget that in the presence of certain gynecological diseases, physiology and thermal procedures are contraindicated.
























